Algorithmic Trading for Beginners: Complete Guide (2026)
Algorithmic trading—using computer programs to automatically execute trades based on predefined rules—has revolutionized financial markets. What was once exclusive to institutional investors and hedge funds is now accessible to individual traders. But can beginners really succeed with algorithmic trading, or is it too complex for those without programming expertise?
In this comprehensive 2026 guide, we’ll demystify algorithmic trading from the ground up. You’ll learn what algo trading is, how it works, the skills you need, platforms available to beginners, how to build your first automated strategy, proper backtesting methods, common pitfalls to avoid, and a realistic roadmap from complete beginner to profitable algo trader.
Whether you want to automate an existing strategy, build systems from scratch, or simply understand how algorithmic trading works, this guide provides everything you need to get started.
Disclaimer: Algorithmic trading involves substantial risk. This is educational content, not financial advice. Always test strategies thoroughly before risking real capital.
What is Algorithmic Trading?
Algorithmic trading (also called algo trading, automated trading, or systematic trading) is the use of computer programs to execute trades automatically based on predetermined rules and conditions.
The Basic Concept
Instead of:
- Manually watching charts for setups
- Placing trades one by one
- Managing positions manually
- Making emotional decisions
You:
- Code your strategy’s rules into a program
- Let the algorithm monitor markets 24/7
- Allow automatic trade execution
- Remove emotions from trading
Simple Example
Manual Trading:
- You watch EUR/USD hourly
- When price crosses above 50 EMA AND RSI > 50
- You manually place a buy order
- You set stop loss and take profit
- You monitor and manage the position
Algorithmic Trading:
if price > EMA_50 and RSI > 50:
buy(EUR_USD, lot_size=0.1, stop_loss=30, take_profit=60)
- The algorithm monitors continuously
- Executes instantly when conditions are met
- Manages position automatically
- No human intervention needed
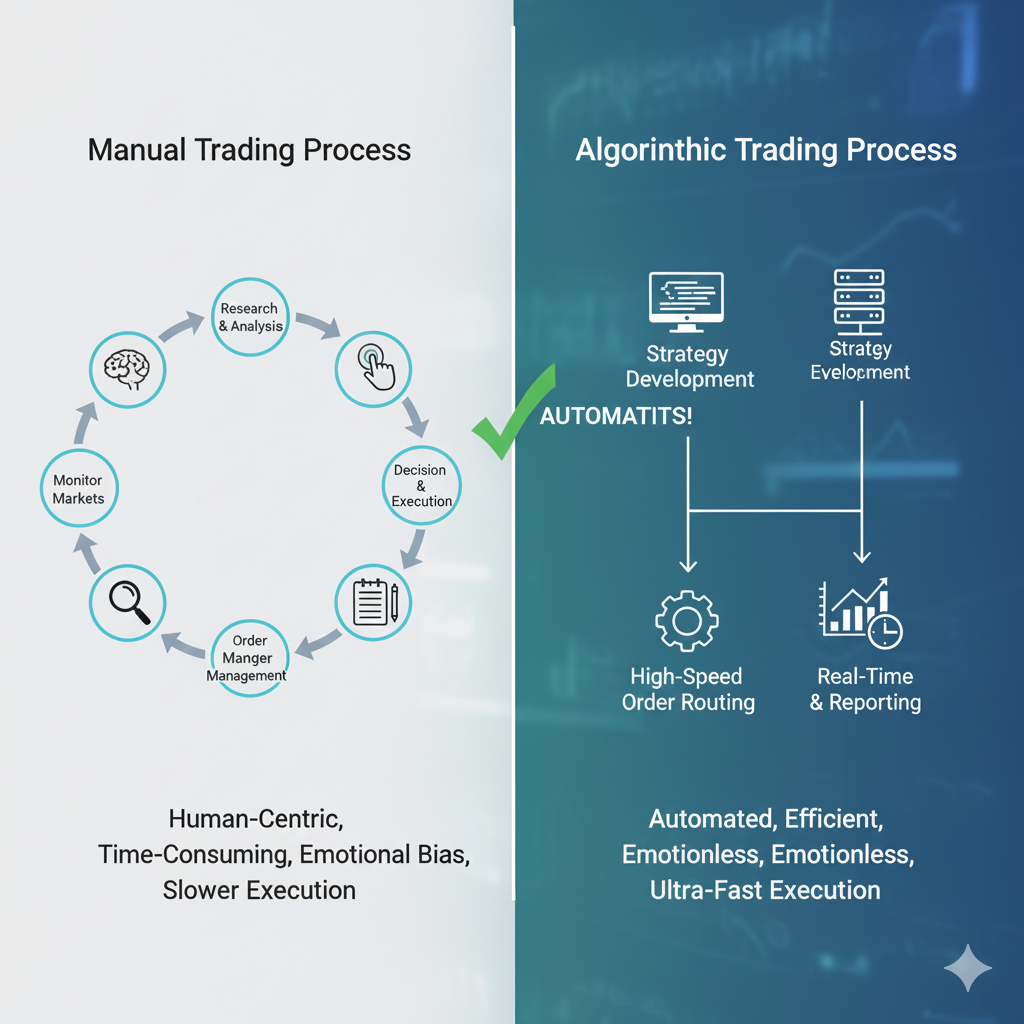
Types of Algorithmic Trading
Not all algorithmic trading is created equal. Understanding the different approaches helps you choose the right path.
1. Fully Automated Trading
Characteristics:
- The algorithm handles everything from signal to execution
- Zero manual intervention required
- Runs 24/7 without supervision
- Makes all trading decisions
Examples:
- High-frequency trading (HFT) systems
- Market-making algorithms
- Statistical arbitrage bots
- Momentum-following systems
Best For: Experienced traders with tested, robust strategies
Risk Level: High (complete trust in algorithm)
2. Semi-Automated Trading
Characteristics:
- The algorithm generates signals
- Human confirms and executes trades
- Combines algorithm efficiency with human judgment
- Trader maintains control
Examples:
- Alert systems (algorithm notifies, you trade)
- Entry automation, but manual exit
- Trade filtering (algo suggests, you decide)
Best For: Beginners and discretionary traders
Risk Level: Medium (human oversight present)
3. Strategy Automation
Characteristics:
- Automates existing manual strategy
- Removes execution delay and emotion
- Follows the rules you already trade manually
- No new strategy development
Examples:
- Automating the 50 EMA bounce strategy
- Coding your pin bar trading rules
- Converting the RSI divergence method to an algorithm
Best For: Traders with proven manual strategies
Risk Level: Lower (automating known approach)
4. High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
Characteristics:
- Thousands of trades per day
- Holds positions for seconds to minutes
- Requires ultra-fast execution
- Sophisticated infrastructure needed
Examples:
- Market making
- Statistical arbitrage
- Latency arbitrage
Best For: Institutions and well-funded professionals
Risk Level: Very high (requires expertise and capital)
Beginner Focus: This guide focuses on types 2 and 3, which are realistic starting points for individual traders.
5-Minute Scalping Strategy for Forex Beginners
Advantages of Algorithmic Trading
Why automate your trading?
Emotional Discipline
✅ No fear – Executes trades even when scary ✅ No greed – Takes profits at predetermined levels ✅ No FOMO – Only trades valid setups ✅ No revenge trading – Follows plan after losses ✅ Consistent execution – Same rules every time
Human Challenge: Emotions sabotage many traders. Algorithms don’t have emotions.
Speed and Efficiency
✅ Instant execution – No hesitation or delay ✅ Simultaneous monitoring – Watches multiple pairs/timeframes ✅ 24/7 operation – Never sleeps, never misses setup ✅ Precise timing – Enters/exits at exact price levels ✅ High-frequency capability – Can trade faster than humans
Human Challenge: Can’t monitor 20 currency pairs across 4 timeframes simultaneously.
Backtesting and Optimization
✅ Test on historical data – Years of trades in minutes ✅ Quantifiable results – Exact win rate, profit factor, drawdown ✅ Objective evaluation – Numbers don’t lie ✅ Strategy refinement – Optimize parameters systematically ✅ Risk analysis – Understand worst-case scenarios
Human Challenge: Can’t manually test thousands of historical setups.
Consistency
✅ Rule adherence – Never skips setups or breaks rules ✅ Position sizing – Always calculates correctly ✅ Risk management – Stops and targets always set ✅ Documentation – Perfect record of every trade ✅ Replicability – Same results every run
Human Challenge: Discretionary deviation from plan is common.
Scalability
✅ Multiple strategies – Run 5-10 different algorithms ✅ Multiple markets – Trade forex, stocks, crypto, commodities ✅ Portfolio approach – Diversify across uncorrelated systems ✅ Efficient capital use – Optimize allocation across strategies
Human Challenge: One person can only actively manage 1-2 strategies.
Disadvantages and Challenges
Algorithmic trading isn’t a magic solution. Understand the challenges.
Technical Complexity
❌ Requires programming – Must learn coding (or hire developer) ❌ Platform learning curve – MetaTrader, Python, etc. take time ❌ System maintenance – Algorithms need updates and monitoring ❌ Technical failures – Internet outages, platform crashes ❌ Debugging needed – Finding and fixing code errors
Reality: Expect a 3-6 months learning curve minimum.
Overfitting Risk
❌ Curve fitting – Optimize for past, fail in future ❌ Data mining bias – Find patterns that were random ❌ False confidence – Backtest looks perfect, live trading fails ❌ Parameter sensitivity – Small changes cause large performance swings
Reality: This is the #1 reason algo strategies fail.
Market Regime Changes
❌ Past ≠ Future – Markets evolve, patterns change ❌ Strategy degradation – What worked stops working ❌ Unexpected events – Algorithms struggle with black swans ❌ Continuous monitoring – “Set and forget” is dangerous
Reality: Algorithms need ongoing evaluation and adjustment.
Capital and Cost Requirements
❌ VPS costs – Virtual Private Server ($20-100/month) ❌ Data fees – Historical and live data ($50-200/month) ❌ Platform costs – Some platforms charge fees ❌ Development time – Significant time investment ❌ Minimum capital – Need adequate account size ($2,000-10,000+)
Reality: Algo trading has setup and ongoing costs.
Lack of Intuition
❌ No market feel – Can’t sense when conditions change ❌ No discretion – Follows rules even when illogical ❌ No adaptation – Can’t adjust to unusual situations ❌ False signals – Executes technically valid but contextually poor trades
Reality: Algorithms lack human judgment and adaptability.
[LINK PLACEHOLDER: Internal link to “Forex Trading Psychology: Why Discipline Matters”]
Do You Need Programming Skills?
The most common question beginners ask.
The Honest Answer: It Depends
For Simple Automation:
- Programming required: Minimal to none
- Platforms: MetaTrader Strategy Tester (drag-and-drop MQL)
- Learning time: 2-4 weeks
- Limitations: Basic strategies only, limited customization
For Moderate Complexity:
- Programming required: Basic to intermediate
- Languages: MQL4/MQL5 (MetaTrader), Pine Script (TradingView)
- Learning time: 2-3 months
- Capabilities: Most strategies, decent customization
For Advanced Systems:
- Programming required: Intermediate to advanced
- Languages: Python, C++, Java
- Learning time: 6-12 months
- Capabilities: Full control, professional-grade systems
Programming Language Comparison
MQL4/MQL5 (MetaTrader):
- Difficulty: Moderate
- Use case: Forex-specific automation
- Pros: Built for trading, large community, many examples
- Cons: Only works in MetaTrader, limited beyond forex
Pine Script (TradingView):
- Difficulty: Easy to moderate
- Use case: Indicators and simple strategies
- Pros: Beginner-friendly, visual, great for learning
- Cons: Limited live execution capabilities
Python:
- Difficulty: Moderate
- Use case: Professional algo trading, backtesting, analysis
- Pros: Most flexible, huge library ecosystem, industry standard
- Cons: Steeper learning curve, requires broker API integration
R:
- Difficulty: Moderate to hard
- Use case: Statistical analysis and backtesting
- Pros: Excellent for quantitative analysis
- Cons: Slower execution, less trading-focused
C++ / Java:
- Difficulty: Hard
- Use case: High-frequency trading, institutional systems
- Pros: Fastest execution, maximum control
- Cons: Very steep learning curve, overkill for beginners
Can You Succeed Without Coding?
Yes, but with limitations:
Option 1: No-Code Platforms
- MetaTrader Strategy Tester (visual mode)
- cTrader Automate (cAlgo, easier than MQL)
- Amibroker (formula language, simpler)
- Limitation: Less flexibility, basic strategies only
Option 2: Hire a Developer
- Freelancer platforms (Upwork, Fiverr)
- MQL5 freelance marketplace
- Cost: $100-5,000+ depending on complexity
- Limitation: Expensive, requires clear specifications, ongoing costs
Option 3: Pre-Built Systems
- Purchase Expert Advisors (EAs) from marketplace
- Cost: $50-500 each
- Limitation: Black box (don’t know how it works), often overfit, many scams
Our Recommendation: Learn basic programming. It’s easier than you think and invaluable long-term. Start with MQL4/5 or Pine Script.
Popular Algorithmic Trading Platforms
Where can beginners start?
1. MetaTrader 4/5 (Most Popular for Forex)
Overview:
- Industry standard for forex algo trading
- Built-in programming (MQL4/MQL5)
- Strategy Tester for backtesting
- Free to use
Best For:
- Forex traders
- Beginners to intermediates
- Those wanting an established platform
Learning Curve: Moderate (2-3 months to proficiency)
Pros: ✅ Huge community and resources ✅ Thousands of free indicators/EAs ✅ Integrated with most forex brokers ✅ Powerful backtesting ✅ Visual strategy builder (limited)
Cons: ❌ MQL language specific to MetaTrader ❌ Limited to forex/CFDs ❌ MT4 outdated (though still popular) ❌ Optimization can be slow
Cost: Free (from broker)
IC Markets Review: Best Broker for Algorithmic Trading?
2. TradingView (Best for Learning)
Overview:
- Web-based charting and analysis
- Pine Script programming language
- Social trading community
- Beautiful interface
Best For:
- Complete beginners
- Learning to code strategies
- Visual backtesting
- Indicator development
Learning Curve: Easy (1-2 months)
Pros: ✅ Easiest programming language ✅ Immediate visual feedback ✅ Great educational resources ✅ Works in browser (no installation) ✅ Beautiful charts
Cons: ❌ Limited live trading execution ❌ Requires broker integration for automation ❌ Not suitable for high-frequency trading
Cost: Free (basic), $12.95-59.95/month (premium)
3. QuantConnect (Best for Python)
Overview:
- Cloud-based algorithmic trading platform
- Python and C# support
- Institutional-grade infrastructure
- Open-source community
Best For:
- Those learning Python
- Serious algo traders
- Multi-asset strategies
- Research and development
Learning Curve: Moderate to hard (3-6 months)
Pros: ✅ Industry-standard Python ✅ Supports stocks, forex, crypto, futures ✅ Powerful backtesting engine ✅ Free to use (basic tier) ✅ Great for portfolio strategies
Cons: ❌ Requires Python knowledge ❌ More complex than MT4/5 ❌ Live trading has monthly fees ❌ Steeper learning curve
Cost: Free (paper trading), $8-250/month (live trading)
4. cTrader (User-Friendly Alternative)
Overview:
- Modern trading platform
- cAlgo for algorithmic trading (C#)
- Clean interface
- Growing popularity
Best For:
- Traders wanting modern UI
- C# programmers
- Those dissatisfied with MetaTrader
Learning Curve: Moderate (2-3 months)
Pros: ✅ More user-friendly than MetaTrader ✅ Modern, intuitive interface ✅ Built-in optimization tools ✅ Good documentation
Cons: ❌ Smaller community than MT4/5 ❌ Fewer brokers support it ❌ Fewer third-party resources
Cost: Free (from broker)
5. NinjaTrader (For Futures/Stocks)
Overview:
- Popular for futures trading
- C# programming (NinjaScript)
- Advanced charting
- Primarily US markets
Best For:
- Futures traders
- Stock traders
- US market focus
Learning Curve: Moderate (2-4 months)
Pros: ✅ Excellent for futures ✅ Advanced features ✅ Professional-grade tools ✅ Active community
Cons: ❌ Focused on US markets ❌ Less suitable for forex ❌ Licensing costs
Cost: Free (simulation), $720-1,320/year (live)
Beginner Recommendation
Start with: TradingView (Pine Script)
- Why: Easiest to learn, immediate visual results, great for understanding concepts
Then graduate to: MetaTrader 4/5 (MQL4/5)
- Why: Industry standard for forex, necessary for real automation
Eventually consider: Python (QuantConnect or custom)
- Why: Most flexible, professional standard, multi-asset capability
Building Your First Algorithm: Step-by-Step
Let’s create a simple algorithm from scratch.
Step 1: Define Your Strategy
Bad approach: “I’ll code something that makes money” Good approach: “I’ll automate my proven 50 EMA bounce strategy”
Strategy Example: 50 EMA Pullback
- Entry: Price pulls back to 50 EMA in uptrend, bullish candle closes
- Stop Loss: 20 pips below 50 EMA
- Take Profit: 40 pips (2:1 risk-reward)
- Timeframe: 4-hour chart
- Pair: EUR/USD
Write it out in plain English before coding!
50 EMA Trading Strategy: Simple Yet Powerful
Step 2: Break Down into Logical Components
Components needed:
- Calculate 50 EMA
- Identify trend direction (price above/below EMA)
- Detect pullback to EMA
- Confirm bullish/bearish candle
- Check if we already have open position
- Calculate position size
- Place trade with stop loss and take profit
- Manage open positions
Step 3: Pseudocode (Human-Readable Logic)
FOR each new candle:
IF no position is currently open:
Calculate 50_EMA
IF price is above 50_EMA (uptrend):
IF previous candle touched 50_EMA:
IF current candle closed bullish:
entry_price = current_close
stop_loss = entry_price - 20_pips
take_profit = entry_price + 40_pips
BUY(lot_size, stop_loss, take_profit)
ELSE IF price is below 50_EMA (downtrend):
IF previous candle touched 50_EMA:
IF current candle closed bearish:
entry_price = current_close
stop_loss = entry_price + 20_pips
take_profit = entry_price - 40_pips
SELL(lot_size, stop_loss, take_profit)
Step 4: Actual Code (MQL4 Example)
// Simple 50 EMA Pullback EA (Expert Advisor)
// This is a beginner example - real systems need more validation
// Input parameters (easily adjustable)
input int EMA_Period = 50;
input int StopLoss_Pips = 20;
input int TakeProfit_Pips = 40;
input double LotSize = 0.1;
// Main function that runs on every tick
void OnTick()
{
// Only trade on new candle (not every tick)
if (!IsNewCandle()) return;
// Check if we already have a position
if (PositionsTotal() > 0) return;
// Calculate 50 EMA
double ema = iMA(_Symbol, PERIOD_H4, EMA_Period, 0, MODE_EMA, PRICE_CLOSE, 0);
// Get current and previous candle data
double close_current = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_H4, 0);
double close_previous = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_H4, 1);
double open_current = iOpen(_Symbol, PERIOD_H4, 0);
double low_previous = iLow(_Symbol, PERIOD_H4, 1);
double high_previous = iHigh(_Symbol, PERIOD_H4, 1);
// Check for BULLISH setup
if (close_previous > ema) // Uptrend
{
if (low_previous <= ema) // Pullback touched EMA
{
if (close_current > open_current) // Bullish candle
{
// Place BUY order
double sl = close_current - StopLoss_Pips * Point * 10;
double tp = close_current + TakeProfit_Pips * Point * 10;
OrderSend(_Symbol, OP_BUY, LotSize, Ask, 3, sl, tp, "50 EMA Buy", 0, 0, clrGreen);
}
}
}
// Check for BEARISH setup
else if (close_previous < ema) // Downtrend
{
if (high_previous >= ema) // Pullback touched EMA
{
if (close_current < open_current) // Bearish candle
{
// Place SELL order
double sl = close_current + StopLoss_Pips * Point * 10;
double tp = close_current - TakeProfit_Pips * Point * 10;
OrderSend(_Symbol, OP_SELL, LotSize, Bid, 3, sl, tp, "50 EMA Sell", 0, 0, clrRed);
}
}
}
}
// Helper function to detect new candle
bool IsNewCandle()
{
static datetime last_time = 0;
datetime current_time = iTime(_Symbol, PERIOD_H4, 0);
if (last_time != current_time)
{
last_time = current_time;
return true;
}
return false;
}
Note: This is simplified for education. Production code needs error handling, money management, trailing stops, and more validation.
Step 5: Test in Strategy Tester
- Open MetaTrader Strategy Tester (Ctrl+R)
- Select your EA (Expert Advisor)
- Choose EUR/USD, H4 timeframe
- Set date range (1-2 years minimum)
- Run backtest
- Analyze results
Step 6: Analyze Results
Key metrics to check:
- Total trades: Need 30+ for statistical significance
- Win rate: 50-70% typical
- Profit factor: >1.3 desirable
- Maximum drawdown: <30% acceptable
- Average win vs average loss: Aim for win > loss
- Consecutive losses: Can your account survive worst streak?
Step 7: Optimize (Carefully!)
Parameters to test:
- EMA period (45, 50, 55)
- Stop loss (15, 20, 25 pips)
- Take profit (30, 40, 50 pips)
Warning: Don’t over-optimize! Test reasonable ranges only.
Step 8: Forward Test
- Run on demo account for 1-3 months
- Compare live results to backtest
- If similar: Strategy may be robust
- If drastically different: Likely overfit
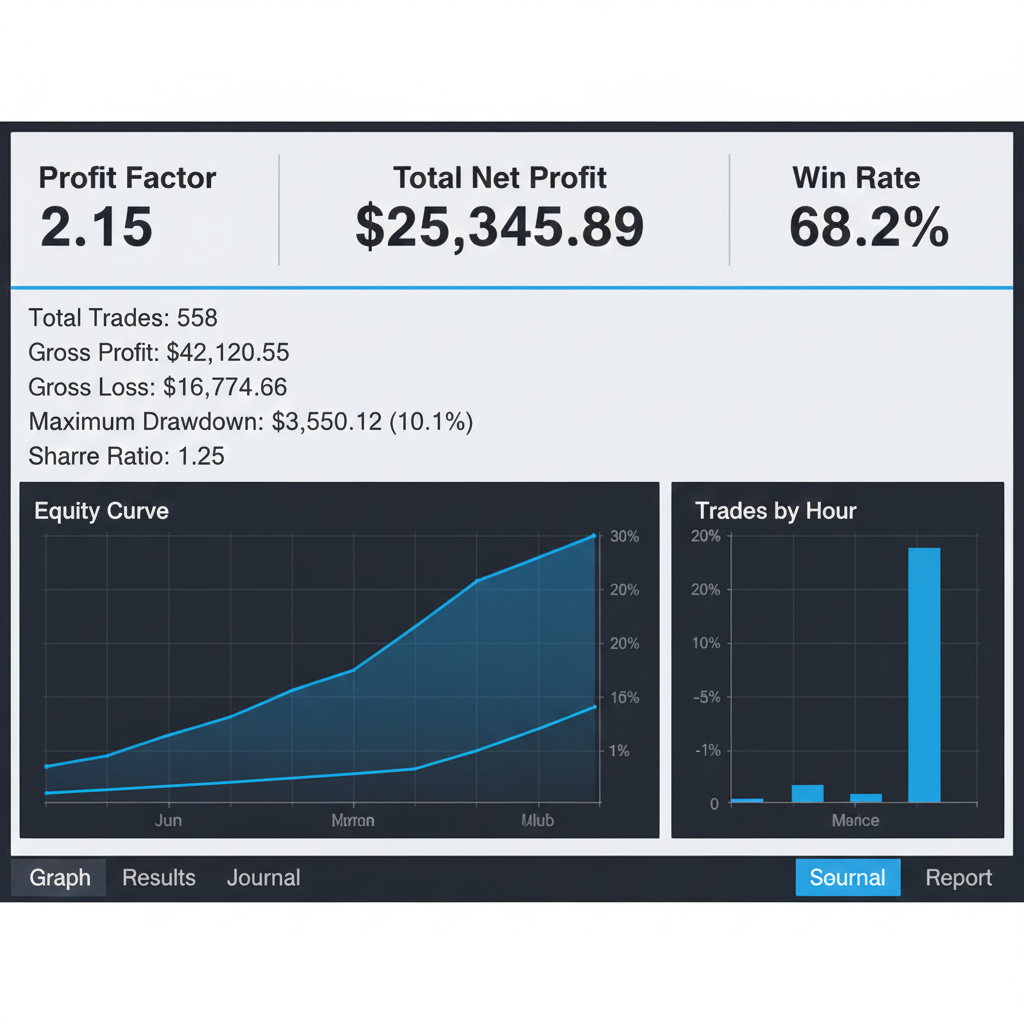
Backtesting: The Critical Skill
Backtesting separates profitable algorithms from garbage.
What is Backtesting?
Definition: Running your algorithm on historical price data to see how it would have performed in the past.
Purpose:
- Validate strategy logic works
- Estimate expected returns
- Identify weaknesses
- Calculate risk metrics
- Build confidence before risking real money
Proper Backtesting Methodology
1. Use Quality Data
- Tick data (most accurate) or M1 data minimum
- From reputable source (broker or paid data provider)
- Sufficient history (3-5 years minimum)
- Include weekends and holidays (realistic gaps)
2. Account for Transaction Costs
- Spreads (realistic, not “from 0.0 pips”)
- Commissions if applicable
- Slippage (1-3 pips average)
- Swap rates for overnight holds
3. Out-of-Sample Testing
- Split data: 70% training, 30% testing
- Optimize on training set only
- Validate on testing set (data algorithm never saw)
- If test set fails, algorithm is overfit
4. Walk-Forward Analysis
- Most robust method
- Optimize on first period, test on next period
- Roll forward, repeat
- If performance degrades rapidly: Overfitting
5. Monte Carlo Simulation
- Randomize trade order thousands of times
- Tests robustness to different sequences
- Generates range of possible outcomes
- Reveals sensitivity to luck
Common Backtesting Mistakes
❌ Mistake 1: Look-Ahead Bias
- Using future information in past decisions
- Example: Using close price before candle completes
- Fix: Only use data available at decision time
❌ Mistake 2: Survivorship Bias
- Testing only on pairs that currently exist/trade well
- Ignores failed/delisted pairs
- Fix: Include all pairs that existed during test period
❌ Mistake 3: Curve Fitting
- Over-optimizing parameters to fit historical data
- Example: Testing EMA periods 1-200 and choosing best
- Fix: Test reasonable ranges based on logic, not maximum performance
❌ Mistake 4: Ignoring Regime Changes
- Markets in 2015 ≠ markets in 2025
- Fix: Test across different market conditions (trending, ranging, volatile, calm)
❌ Mistake 5: Cherry-Picking Time Periods
- Testing only on periods where strategy worked
- Fix: Use continuous multi-year periods, test through 2008 crisis, 2020 COVID, etc.
❌ Mistake 6: Perfect Execution Assumption
- Assuming instant fills at exact prices
- Fix: Model realistic slippage and rejection rates
Interpreting Backtest Results
Good Signs: ✅ Consistent performance across different years ✅ Similar results on in-sample and out-of-sample data ✅ Profit factor >1.5 ✅ Win rate appropriate for strategy type ✅ Maximum drawdown survivable ✅ Works on multiple currency pairs (if designed to)
Red Flags: 🚩 Too good to be true (90%+ win rate, <5% drawdown) 🚩 Dramatically different in-sample vs out-of-sample 🚩 Works only on one specific timeframe/pair 🚩 Requires exact parameters (sensitive to small changes) 🚩 Long periods of no trades or only losses 🚩 Profit comes from one or two lucky trades
[LINK PLACEHOLDER: Internal link to “Risk Management in Forex: The Ultimate Guide”]
Common Algo Trading Strategies
Popular approaches beginners can implement.
1. Trend Following
Concept: Identify trend, enter pullbacks, ride the trend
Example:
- 50 EMA strategy (we coded earlier)
- Moving average crossovers (50 MA crosses 200 MA)
- Donchian channel breakouts
Pros:
- Simple logic
- Works in trending markets
- Can capture large moves
Cons:
- Fails in ranging markets (whipsaws)
- Late entries common
- Requires patience
Typical Performance: 40-50% win rate, but winners 2-3× losers
2. Mean Reversion
Concept: Price deviates from average, revert to mean
Example:
- Bollinger Bands (buy at lower band, sell at upper)
- RSI extremes (buy <30, sell >70)
- Standard deviation moves
Pros:
- High win rate (60-70%)
- Works in ranging markets
- Quick trades
Cons:
- Small wins, occasional large losses
- Fails in strong trends
- Requires tight risk management
Typical Performance: 60-70% win rate, winners ≈ losers
3. Breakout Trading
Concept: Trade breakouts from consolidation
Example:
- Support/resistance breaks
- Triangle pattern breakouts
- Range breakouts
Pros:
- Catches explosive moves
- Clear entry levels
- Good risk-reward potential
Cons:
- Many false breakouts
- Requires confirmation
- Timing critical
Typical Performance: 35-45% win rate, winners 3-5× losers
4. Grid Trading
Concept: Place buy/sell orders at intervals creating “grid”
Example:
- Buy every 20 pips below current price
- Sell every 20 pips above
- Profit from oscillation
Pros:
- No directional bias needed
- Profits in ranging markets
- Can be automated easily
Cons:
- DANGEROUS in trending markets
- Can lead to massive drawdowns
- Requires large capital
- Not recommended for beginners
5. Arbitrage
Concept: Exploit price differences between markets
Example:
- Same pair different brokers
- Correlated pairs (EUR/USD vs GBP/USD)
- Triangular arbitrage (EUR/USD, USD/JPY, EUR/JPY)
Pros:
- Theoretically low risk
- Market neutral
Cons:
- Requires ultra-fast execution
- Opportunities rare and brief
- Needs significant capital
- Brokers may restrict
- Extremely difficult for retail traders
Beginner Recommendation: Start with trend following or mean reversion. Avoid grid and arbitrage initially.
Live Trading: Making the Leap
You’ve backtested successfully. Now what?
The Transition Process
Step 1: Paper Trade (1-3 Months)
- Run algorithm on demo account
- Use realistic capital amount
- Monitor daily performance
- Compare to backtest expectations
- Critical: If live results differ significantly from backtest, DO NOT proceed to real money
Step 2: Start Micro (Month 4-6)
- Smallest position sizes possible
- Risk 0.25-0.5% per trade (half normal)
- Monitor extremely closely
- Focus on: execution quality, slippage, fill rates
- Goal: Verify algorithm works in live conditions
Step 3: Scale Gradually (Month 7-12)
- Increase position sizes slowly (10-20% monthly)
- Reach full 1-2% risk per trade over 6 months
- Continue monitoring and validation
- Be ready to stop/reduce if performance degrades
Step 4: Optimization and Refinement (Ongoing)
- Review performance monthly
- Adjust parameters if needed (conservatively)
- Watch for strategy degradation
- Consider additional strategies for diversification
Infrastructure Requirements
1. Virtual Private Server (VPS)
- Why: 24/7 uptime, no interruptions
- Cost: $20-100/month
- Providers: Forex VPS, Vultr, DigitalOcean, AWS
- Essential for: Fully automated strategies
2. Reliable Internet
- Why: Avoid disconnections during critical moments
- Backup: Mobile hotspot as failsafe
- Speed: Minimum 10 Mbps
3. Broker Selection
- Fast execution (critical for algos)
- Allows automated trading (some brokers restrict)
- Low latency servers
- Transparent pricing
- Recommended: IC Markets, Pepperstone for algo trading
4. Monitoring System
- Alerts: Email/SMS when trades execute or errors occur
- Dashboard: Track performance real-time
- Logs: Keep detailed trade logs for review
Risk Management for Algo Trading
Daily Loss Limit:
- Shut down algorithm if loses X% in one day
- Typical: 2-3% daily maximum
- Prevents cascade failures
Position Limits:
- Maximum positions open simultaneously
- Prevents over-leverage
- Typical: 3-5 positions maximum
Correlation Management:
- Don’t trade highly correlated pairs simultaneously
- EUR/USD + GBP/USD = correlated
- Diversify across uncorrelated strategies/pairs
Manual Override:
- Always have kill switch to stop algorithm
- Monitor major news events (NFP, Fed meetings)
- Consider pausing during extreme volatility
Regular Review:
- Check performance weekly minimum
- Monthly deep analysis
- Quarterly strategy review
- Annual complete evaluation
[LINK PLACEHOLDER: Internal link to “How to Choose the Best Forex Broker for Algorithmic Trading”]
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Learn from others’ mistakes.
Pitfall #1: Overfitting (The Big One)
The Problem: Creating algorithm that works perfectly on past data but fails miserably on new data.
How it Happens:
- Testing 100+ parameter combinations
- Choosing the best performing set
- Not validating on out-of-sample data
How to Avoid: ✅ Limit parameter optimization to logical ranges ✅ Always test on out-of-sample data ✅ Use walk-forward analysis ✅ If it looks too good to be true, it is ✅ Prefer robustness over maximum backtest return
Pitfall #2: Inadequate Capital
The Problem: Starting algo trading with insufficient funds to survive normal drawdowns.
Why it Matters: Even good strategies have 20-30% drawdowns. With $500 account, 30% = $150, leaving $350. A few more losing trades and account is crippled.
Minimum Capital Recommendations:
- For learning: $500-1,000 (accept you might lose it)
- For serious algo trading: $2,000-5,000 minimum
- For comfortable operation: $10,000+
How to Avoid: ✅ Save until you have adequate capital ✅ Use micro/cent accounts while building capital ✅ Consider prop firm challenges (risk challenge fee, not trading capital)
Pitfall #3: No Risk Management
The Problem: Algorithm trades without proper stop losses, position sizing, or exposure limits.
Consequences:
- One bad trade wipes out months of profits
- Account blown during unexpected event
- Overleveraging leads to margin calls
How to Avoid: ✅ Always code stop losses into algorithm ✅ Calculate position sizes based on account % risk ✅ Implement daily/weekly loss limits ✅ Cap total exposure (max positions, total risk) ✅ Test risk management in backtest
Pitfall #4: Ignoring Transaction Costs
The Problem: Backtests show profitability, but live trading loses money due to spreads, commissions, slippage.
Example:
- Backtest: 30 pip average profit per trade
- Live: 2 pip spread + 1 pip slippage + commission = -5 pips
- Real profit: 25 pips (17% less than expected)
- High-frequency strategies especially vulnerable
How to Avoid: ✅ Model realistic spreads in backtests (not “from 0 pips”) ✅ Add 1-2 pips slippage to backtest ✅ Include commission costs ✅ Choose broker with tight spreads for algos ✅ Avoid strategies with small profit targets (<10 pips)
Pitfall #5: Set-and-Forget Mentality
The Problem: Treating algo trading as passive income requiring no monitoring.
Reality:
- Markets change, strategies degrade
- Technical failures occur
- Broker issues happen
- Black swan events strike
How to Avoid: ✅ Monitor performance daily ✅ Set up alerts for errors and unusual activity ✅ Review trades weekly ✅ Be ready to pause or stop algorithm ✅ Have manual override capability
Pitfall #6: Strategy Degradation Denial
The Problem: Algorithm that worked for months starts losing, but trader keeps running it hoping it recovers.
Why it Happens:
- Emotional attachment to system
- Denial that markets have changed
- Hope it’s just a “bad period”
How to Avoid: ✅ Define performance benchmarks ✅ Stop algorithm if underperforms X months ✅ Regular review and honest assessment ✅ Accept that strategies have lifecycles ✅ Diversify across multiple strategies
Pitfall #7: Black Box Trading
The Problem: Using purchased EA (Expert Advisor) or indicator without understanding how it works.
Dangers:
- Can’t evaluate if it’s broken
- Don’t know when market conditions invalidate it
- Can’t fix problems
- Often scams or overfit systems
How to Avoid: ✅ Only trade algorithms you understand ✅ Build your own or hire developer with full transparency ✅ Avoid “magic” EAs from marketplaces ✅ Understand the logic behind every rule

Your 12-Month Roadmap to Algo Trading
Realistic timeline from beginner to competent algo trader.
Month 1-2: Foundation Building
Learn:
- Basic trading concepts (if not already known)
- Technical analysis fundamentals
- Risk management principles
- How algorithms work (conceptually)
Practice:
- Trade manually to develop strategy
- Keep detailed journal
- Identify patterns in your trading
Resources:
- Our strategy guides (5-min scalping, 50 EMA, RSI divergence)
- Trading books (Technical Analysis, Market Wizards)
- YouTube tutorials on algo trading
Goal: Understand trading and identify strategy to automate
Month 3-4: Platform and Programming Basics
Learn:
- Choose platform (start with TradingView or MetaTrader)
- Basic programming in chosen language
- Platform-specific tutorials
- Simple code examples
Practice:
- Follow coding tutorials
- Modify existing indicators
- Write simple scripts (calculate EMA, plot lines)
Resources:
- TradingView Pine Script documentation
- MQL4/5 tutorial series
- Codecademy Python basics (if going Python route)
Goal: Write and run your first simple indicator
Month 5-6: Building First Algorithm
Learn:
- How to translate strategy to code
- Backtesting methodology
- Debugging techniques
Practice:
- Code your manual strategy
- Run backtests
- Fix errors and refine
- Compare to manual trading results
Resources:
- Strategy Tester guides
- Backtesting tutorials
- Community forums for help
Goal: Complete working algorithm with backtest results
Month 7-8: Validation and Testing
Learn:
- Out-of-sample testing
- Walk-forward analysis
- Overfitting detection
- Performance metrics analysis
Practice:
- Rigorous backtesting
- Test on multiple pairs/timeframes
- Sensitivity analysis
- Statistical validation
Resources:
- Quantitative trading books
- Backtesting best practices guides
- Statistics refresher
Goal: Validated algorithm ready for paper trading
Month 9-10: Paper Trading
Learn:
- Live market behavior vs backtest
- Slippage and execution issues
- Monitoring and maintenance
- Error handling
Practice:
- Run algorithm on demo account
- Monitor daily performance
- Compare to backtest expectations
- Adjust and refine
Resources:
- Demo accounts (free from brokers)
- Performance tracking tools
- Trading journals
Goal: Successful 2-3 month paper trading period
Month 11-12: Micro Live Trading
Learn:
- Position sizing for real money
- Emotional discipline (yes, even with algos!)
- Live trading logistics
- VPS setup and management
Practice:
- Trade smallest sizes possible
- Gradual capital increase
- Real-world problem solving
- Performance analysis
Resources:
- VPS providers
- Broker support
- Algo trading communities
Goal: Profitable first 2-3 months of live trading
Month 13+: Scale and Diversify
Learn:
- Portfolio management
- Multiple strategy coordination
- Advanced optimization
- Strategy development
Practice:
- Gradually increase position sizes
- Develop additional strategies
- Diversify across pairs/timeframes
- Continuous improvement
Goal: Consistent profitability and expanding system
Reality Check: This timeline assumes dedicated effort (5-10 hours/week). Some take longer, a few progress faster. Don’t rush—it’s a marathon, not a sprint.
Tools and Resources for Learning
Where to learn algorithmic trading.
Free Learning Resources
Websites:
- QuantConnect Learn (Python algo trading)
- MQL5 Community (MQL tutorials and forums)
- TradingView Pine Script documentation
- BabyPips (forex basics)
YouTube Channels:
- TheMovingAverage (MQL5 tutorials)
- TradingRiot (algo trading strategies)
- Part Time Larry (QuantConnect tutorials)
- ForexBoat (MQL4 basics)
Books (Essential):
- “Algorithmic Trading” by Ernest Chan
- “Building Winning Algorithmic Trading Systems” by Kevin Davey
- “Quantitative Trading” by Ernest Chan
- “Trading Systems” by Emilio Tomasini
Communities:
- r/algotrading (Reddit)
- Elite Trader forums
- MQL5 community
- QuantConnect forums
Paid Resources (Optional but Valuable)
Courses:
- QuantInsti EPAT Program ($2,000-3,000) – Professional certification
- Udemy algorithmic trading courses ($50-200)
- TradingView course offerings
- Specialized bootcamps ($500-2,000)
Tools:
- Historical data (Dukascopy, FXCM, etc.)
- Advanced backtesting software (StrategyQuant, Amibroker)
- Analytics platforms (MyFXBook, FX Blue)
Mentorship:
- One-on-one coaching ($1,000-5,000)
- Trading groups with algo focus ($50-200/month)
Our Recommendation: Start with free resources. Invest in paid education only after demonstrating commitment through 3-6 months of self-study.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can beginners really succeed with algorithmic trading?
Yes, but with realistic expectations and significant effort. Success requires 6-12 months of learning (programming, strategy development, backtesting) before going live. Most beginners fail because they underestimate the complexity or expect quick results. Those who succeed treat it as a serious skill to develop over 1-2 years, not a get-rich-quick scheme. Starting with simple strategies, thorough testing, and small position sizes dramatically improves odds of success.
Do I need to know programming to start algo trading?
Not necessarily, but it’s highly recommended. You can use visual/drag-and-drop tools (MetaTrader Strategy Tester visual mode), hire developers, or buy pre-made Expert Advisors (EAs). However, these approaches have significant limitations. Learning basic programming (MQL4/5 or Pine Script) takes 2-3 months and provides control, understanding, and lifetime capability. Most successful algo traders learned programming—it’s the better long-term investment.
How much money do I need to start algorithmic trading?
Minimum $500-1,000 for learning and testing, but $2,000-5,000 is recommended for serious algo trading. Small accounts can’t survive normal drawdowns (20-30%), making recovery difficult. Additionally, you need capital for VPS ($20-100/month), data if required, and platform fees. Many successful algo traders started with $5,000-10,000. You can learn with less, but scaling profitably requires adequate capital.
What is the best platform for beginner algo traders?
TradingView (Pine Script) for learning concepts due to easy syntax and visual feedback. MetaTrader 4/5 (MQL4/5) for serious forex algo trading due to industry standard status and broker integration. Python (QuantConnect) for professional multi-asset trading. Start with TradingView to learn, transition to MetaTrader for real automation. Choose based on your goals: forex = MT4/5, multi-asset = Python, learning = TradingView.
How long does it take to build a profitable trading algorithm?
Realistically 6-12 months from zero knowledge to profitable live trading. Breakdown: 2-3 months learning platform and programming, 2-3 months developing and backtesting strategy, 2-3 months paper trading and validation, 1-2 months micro live trading before scaling. Those claiming “profitable in 30 days” either got lucky (unsustainable) or are selling something. Treat algorithmic trading as a professional skill requiring serious time investment.
Can I make money with algorithmic trading?
Yes, but realistic expectations are crucial. Professional retail algo traders achieve 10-30% annual returns, not 100%+ as marketed. Institutional algorithms with massive resources achieve 15-50% annually. Getting to consistent profitability takes 12-24 months of development. Most beginners (70-80%) fail or give up before achieving consistency. Success requires programming skills, trading knowledge, discipline, adequate capital, and patience.
Are algorithmic trading signals and bots worth buying?
Generally, no. Most sold EAs and bots are either scams, overfit systems with impressive backtests but poor live performance, or basic strategies you could build yourself. The few legitimate systems are expensive ($500-5,000+) and still require understanding to use properly. If a bot truly worked well, the creator would trade it themselves rather than selling it. Learn to build your own—it’s more valuable long-term than buying black boxes.
Conclusion: Your Path to Algorithmic Trading Success
Algorithmic trading offers genuine advantages: emotion-free execution, 24/7 market monitoring, precise backtesting, and the ability to implement strategies beyond human speed and consistency. But it’s not a magic solution or passive income generator.
The Reality:
Algorithmic trading is: ✅ A learnable skill with 6-12 month learning curve ✅ Powerful for disciplined strategy execution ✅ Excellent for removing emotions from trading ✅ Viable for achieving 10-30% annual returns ✅ Scalable across multiple strategies and markets
Algorithmic trading is NOT: ❌ A get-rich-quick scheme ❌ Passive income requiring no monitoring ❌ Guaranteed profits or “Holy Grail” ❌ Easy money with no learning required ❌ Replacement for trading knowledge
Your Success Depends On:
- Solid Trading Foundation – Understand markets before automating
- Programming Skills – Basic to intermediate coding ability
- Rigorous Testing – Proper backtesting prevents disasters
- Realistic Expectations – 10-30% annually, not 100%+
- Adequate Capital – $2,000-5,000+ minimum for serious attempt
- Patience and Discipline – 12-24 months to profitability
- Continuous Learning – Markets evolve, strategies must adapt
Our Recommendation:
Month 1-3: Learn manual trading first
- Use our free strategy guides
- Practice on demo accounts
- Develop consistent approach
Month 4-6: Learn programming basics
- Start with TradingView or MetaTrader
- Follow tutorials, modify examples
- Build simple indicators
Month 7-12: Develop your first algorithm
- Automate proven manual strategy
- Backtest rigorously
- Paper trade 2-3 months
Month 13+: Scale carefully
- Start with micro positions
- Monitor closely
- Grow gradually as performance proves consistent
The Hard Truth:
Most beginners fail at algo trading because they:
- Skip the learning curve
- Buy pre-made bots that don’t work
- Underestimate complexity
- Overtrade or overlever age
- Give up too quickly
But those who succeed:
- Invest time learning properly
- Build their own systems
- Test rigorously before going live
- Start small and scale gradually
- Treat it as a business, not gambling
Choose education over shortcuts. Choose understanding over black boxes. Choose patience over haste.
The path to algorithmic trading success is clear: learn to trade, learn to code, develop systematically, test thoroughly, start small, and scale cautiously. It’s not easy or quick, but it’s achievable for those willing to put in the work.
Your algorithmic trading journey starts with a single step. Will you take it?
Important Disclaimer:
This guide is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice, investment advice, or trading advice. Algorithmic trading involves substantial risk of loss.
Past performance of backtests does not guarantee future results. Most algorithmic trading strategies eventually fail or require significant modification.
Always thoroughly test strategies before risking real capital. Never risk more than you can afford to lose.
The author and publisher are not responsible for any losses incurred from algorithmic trading based on information in this guide.